Imaging
Patient Scheduling: (775) 445-5500
Imaging Locations & Hours of Operation
Please note each location offers different imaging services, competitive imaging pricing, and access to multidisciplinary specialties.
Carson Tahoe Imaging, a department of Carson Tahoe Regional Healthcare, provides Carson City, Reno, Douglas County, Minden, Gardnerville, Dayton, and Lake Tahoe areas with convenient access to high-quality imaging exams, state-of-the-art technologies, and our expert radiology staff. Our state-of-the-art technologies allow board-certified radiologists, interventional radiologists, and highly skilled licensed technologists to work collaboratively to detect and evaluate diseases and other conditions faster and with more accuracy than ever before. In addition to providing leading-edge clarity and accuracy, Carson Tahoe’s medical imaging modalities are specially designed to maximize patient comfort and reduce exposure to radiation.
All X-ray and imaging locations have undergone a rigorous review process to ensure they meet safety standards.
All Carson Tahoe medical imaging locations have been upgraded with the latest state-of-the-art technologies including:
- Exams including wide bore GE 3T MRI (MR750w), GE 1.5 Tesla (MR450w), GE MRI Excite, 128-slice GE LightSpeed VCT scanning with low-dose technology, 64-slice GE Optima CT 660 with low-dose technology, 64-slice GE LightSpeed with low-dose technology, and ‘Smart Technology’ LOGIQ E9 ultrasound
- The first Patient Caring Suite in Nevada, featuring a GE 3T MRI (MR750w)
- ASiR low dose technology minimizes patient’s exposure to radiation for all exams
- Wide bore MRI and CT with oversized scanning platforms to accommodate larger patients
-
GE MAVRIC SL software provides readable scans for patients with metal implants
Carson Tahoe Breast Center (Mammography, Breast MRI, Stereotactic Breast Biopsy)
Carson Tahoe’s comprehensive Breast Center offers patients a seamless integration of preventive, diagnostic, imaging and surgical services in support of early detection and treatment of breast cancer – all in one, convenient location. Located on the Carson Tahoe Medical Campus, the center operates as an extension of Sierra Surgery and features the latest technological advancements, including 3D mammography, 2D mammography, breast biopsy, and breast MRI.
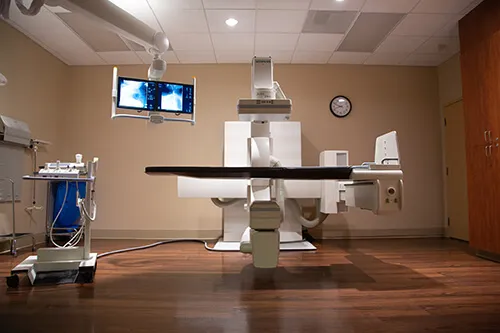
X-Ray (diagnostic X-Ray and digital X-Ray)
An X-ray machine uses a small dose of radiation to produce images also known as a radiograph. X-rays are noninvasive tests that use x-rays, which are passed through the body and captured on a detector from which a digital image is made. X-rays may be performed on any body part. X-rays are a frequent, quick and effective imaging tool utilized for illness or injury evaluation.
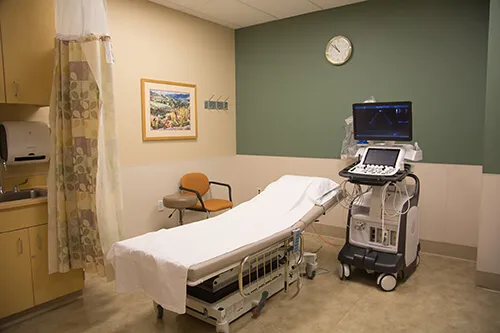
Ultrasound
Ultrasound, also known as Sonogram, uses sound waves to create an image. With ultrasound, water-soluble gel and a probe will be placed on your skin sending sound waves into your body. Those sound waves bounce off your organs and return to the machine creating a diagnostic image. Ultrasound is a very safe technology.
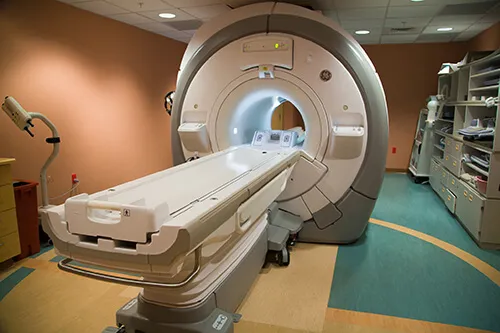
High Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an imaging technique that uses powerful magnets, radio waves and a computer to capture detailed pictures of the inside of your body. MRI helps doctors diagnose a disease or injury and it can monitor how well you are doing with a treatment. MRI exams can be done on different parts of your body. It is especially useful for looking at soft tissues and the nervous system. Unlike X-rays, which use ionizing radiation, MRI uses a non-ionizing approach to image the anatomy within the body. The type of non-ionizing energy is called radio-frequency (RF) waves. Unlike X-rays, RF waves do not break strands of DNA. This is one reason why MRI is a safer alternative as opposed to X-rays, and is a modality of choice for pregnant and pediatric patients. Learn more about your MRI exam here.
Interventional Radiology (IR)
Learn more about our expert radiologists through Tahoe Carson Radiology.
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram also known as an Echo or cardiac ultrasound uses sound waves to produce moving images of your heart. This common test allows your cardiologist to evaluate the size and function of the heart chambers and heart muscle as well as the heart valves. Your cardiologist can use the images from an echocardiogram to identify heart disease. There are a few different types of echocardiograms. During a standard echocardiogram, a registered technician will use a handheld device called a transducer on your chest. It sends high-frequency sound waves that bounce off your heart and reflect back images and sounds of your heart. The transducer will be used across several areas of your chest with a small amount of water-soluble gel. You may be asked to follow some breathing techniques or to move into different positions on the exam table in order for the sonographer to better visualize your heart. During the exam, you may hear sounds coming from the machine that reflect Doppler signals of the blood flow moving through your heart.
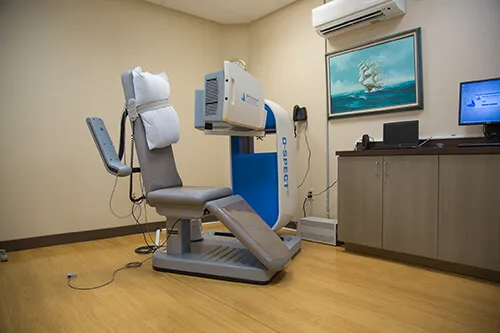
Stress Myocardial Perfusion Imaging
Stress myocardial perfusion imaging is a nuclear cardiology test that shows how well blood flows to the muscle of the heart (the myocardium). A small amount of radioactive tracer lets doctors view heart function using a scanner called a SPECT (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography) camera. Two sets of images are taken; one with the patient at rest and one after stress. There are two types of stress tests: treadmill exercise (standard) and drug-induced stress, if a patient is unable to perform the exercise test due to a physical disability or other reason. The patient’s doctor will determine which of the stress tests is appropriate and further interpret the results. Learn more about prepping for your stress test here.
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear Medicine is one of several imaging modalities of Radiology. Nuclear Medicine uses Radiopharmaceuticals or Radioactive tracers to evaluate the systems of your body. That is what makes Nuclear Medicine different from the other branches of Medical Imaging; the strength of Nuclear Medicine lies in its ability to demonstrate function rather than just anatomy. The radiopharmaceuticals are designed to mimic naturally occurring molecules in your body; therefore there are no side effects from the tracers with which you are injected. Although Nuclear Medicine does use a small amount of Ionizing radiation, the primary isotope used has a half-life of only 6 hours, making it safe to be around others after being injected. Learn more about your Nuclear Medicine exam here. Learn more about prepping for Nuclear Medicine here.
PET/CT
A (PET) scan allows your doctor to check for diseases in your body by using a special dye containing radioactive tracers. Learn more about preparing for your PET/CT scan here. Learn more about prepping for your PET/CT here.
Other X-Ray & Imaging Services at Carson Tahoe Health:
- superDimension™ Electromagnetic Navigation Bronchoscopy (ENB) – LungGPS technology
- Computed Tomography (CT)
- Bone Density (DEXA scan)
- Fluoroscopy
- Venous Ablation
- Balloon Kyphoplasty